Legio

About Legio
Legio is the site of the sprawling base of the Roman VIth Ferrata Legion. Established during the reign of the Emperor Hadrian (117–138 A.D.), the base controlled imperial roads, with direct access to the Galilee and inland valleys of northern Palestine—important centers of the local, occasionally uproarious, Jewish population. Excavations so far have demonstrated clear ties to major political and cultural events in the formative years of Rabbinic Judaism and Christianity and have provided an incredible new window into the Roman military occupation of the eastern provinces.
Research Goals
Coming soon!
publications
M.J. Adams, M. Cradic, Y. Farhi, M. Peers, and Y. Tepper, “A Betyl with a Decorated Base from the Principia of the Roman VIth Ferrata Legionary Base, Legio, Israel,” Israel Museum Studies in Archaeology 9 (2019): 68-92.
Y. Tepper, J. David, and M.J. Adams, “Excavations at the Camp of the Roman Sixth Ferrata Legion at Legio (el-Lajjun), Israel. A Preliminary Report of the 2013 Season,” Strata: The Bulletin of the Anglo-Israel Archaeological Society 34 (2017) 87-120.
R.S. Homsher, B. L. Drake, Y. Tepper, M. J. Adams, and J. K. David, “From the Bronze Age to the ‘Lead Age’. Observations on Sediment Analyses at Two Archaeological Sites in the Jezreel Valley, Israel: the Roman Camp at Legio and the Early Bronze Age Village at Tel Megiddo East,” Mediterranean Archaeology & Archaeometry 16.1 (2016) 187-204. http://maajournal.com/Issues/2016/Vol16-1/Full16.pdf DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.35533
Y. Tepper , J. David, and M.J. Adams, “The Legionary Base of the Roman Sixth Ferrata Legion at Legio, Israel,” Popular Archaeology Magazine 18 (2015)
A. Prins, M.J. Adams, M. Ashley, R.S. Homsher, “Digital Archaeological Fieldwork and the Jezreel Valley Regional Project, Israel,” Near Eastern Archaeology 77:3 (2014) 196-201.
Y. Tepper, "The Tomb of Ephraim Bar-Shimon from Kefar ‘Othnay and the Identity of the Site’s Population in the Roman and Byzantine Periods," in G.C, Bottini, L.D. Chrupcata, J. and Patrich (eds.) Knowledge and Wisdom: Archaeological and Historical Essays in Honour of Leah Di Segni (Studium Biblicum Franciscanum, 54. Milano: Edizioni Terra Santa, 2014): 295-303.
M.J. Adams, J. David, and Y. Tepper, “Legio: Excavations at the Camp of the Roman Sixth Ferrata Legion in Israel,” Biblical Archaeology Society, Bible History Daily website (17 October 2013).



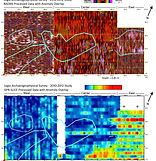
J.Pincus, T. DeSmet, Y. Tepper, and M.J. Adams, “Ground Penetrating Radar and Electromagnetic Archaeogeophysical Investigations at the Roman Legionary Camp at Legio, Israel,” Archaeological Prospection 20.3 (2013) 1-13. DOI: 10.1002/arp.1455. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/arp.1455/abstract .
O. Peleg-Barkat and Y. Tepper, “Engraved Gems from Sites with a Military Presence in Roman Palestine: the Cases of Legio and Aelia Capitolina,” in C. Entwisle and N. Adams (eds.), 'Gems of Heaven': Recent Research on Engraved Gemstones in Late Antiquity c. AD 200-600 (London, 2012): 99–104.
G. Bar-Oz and Y. Tepper,"Out on the Tiles - Animal Footprints from the Roman Site of Kefar ‘Othnay (Legio), Israel," Near Eastern Archaeology 73.4 (2010): 244-247.
Y. Tepper, "The Roman Legionary Camp at Legio, Israel: Results of an Archaeological Survey and Observations on the Roman Military Presence at the Site," in A.S. Lewin and P. Pellegrini (eds.), The Late Roman Army in the East from Diocletian to the Arab Conquest: Proceedings of a Colloquium Held at Potenza, Acerenza and Matera, Italy (May 2005) (BAR International Series, 1717; Oxford: Archaeopress, 2007): 57–71.
Y. Tepper and L. Di Segni, A Christian Prayer Hall of the 3rd Century CE At Kfar ʻOthnai (Legio). Excavations at the Megiddo Prison 2005. Israel Antiquities Authority (2006).
Y. Tepper, "Lajjun – Legio in Israel: Results of a Survey in and Around the Military Camp Area," in P. Freeman, J. Bennett, Z. T. Fiema. and B. Hoffmamm (eds.), Limes XVIII: Proceedings of the XVIIIth Roman International Congress of Roman Frontier Studies (BAR International Series,1084; Oxford, 2002): 231-242.